The Russian budget deficit exceeded $61 billion: what led to the financial crisis


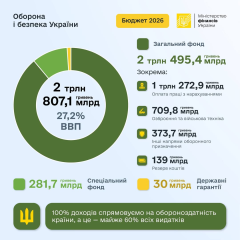
In January–July 2025, the federal budget deficit of Russia rose to $61 billion (2.2% of GDP) compared to the planned $14.66 billion. Following the budget changes in April, the government expected $47.4 billion, but the actual figures exceeded even this forecast, as reported by the Intelligence Service of Ukraine.
'The fall in oil and gas revenues by 18.5% - down to $69 billion - led to the strengthening of the ruble and the decline in global oil prices. An additional factor was the underperformance of the revenue plan: the average annual exchange rate of the ruble ($85.9 per dollar) turned out to be significantly stronger than the $94.3 laid out in the budget. Expenses over 7 months increased by 20.8%, to $314.9 billion,' - explained the intelligence.
At the same time, non-oil and gas revenues of Russia increased by 14% to $185 billion, but this is not enough to compensate for export losses. By the end of the year, the deficit may reach $75 billion. According to the Ukrainian Intelligence Service, the official GDP growth forecast has been revised down from 2.5% to 0.5-1%.
The increase in the budget deficit of Russia in 2025 is associated with a significant drop in oil and gas revenues, the strengthening of the ruble, and the decline in global oil prices. Even with the increase in non-oil and gas revenues, the compensation for export losses was insufficient. The revised official GDP growth forecast indicates the severe economic conditions awaiting Russia.
Read also